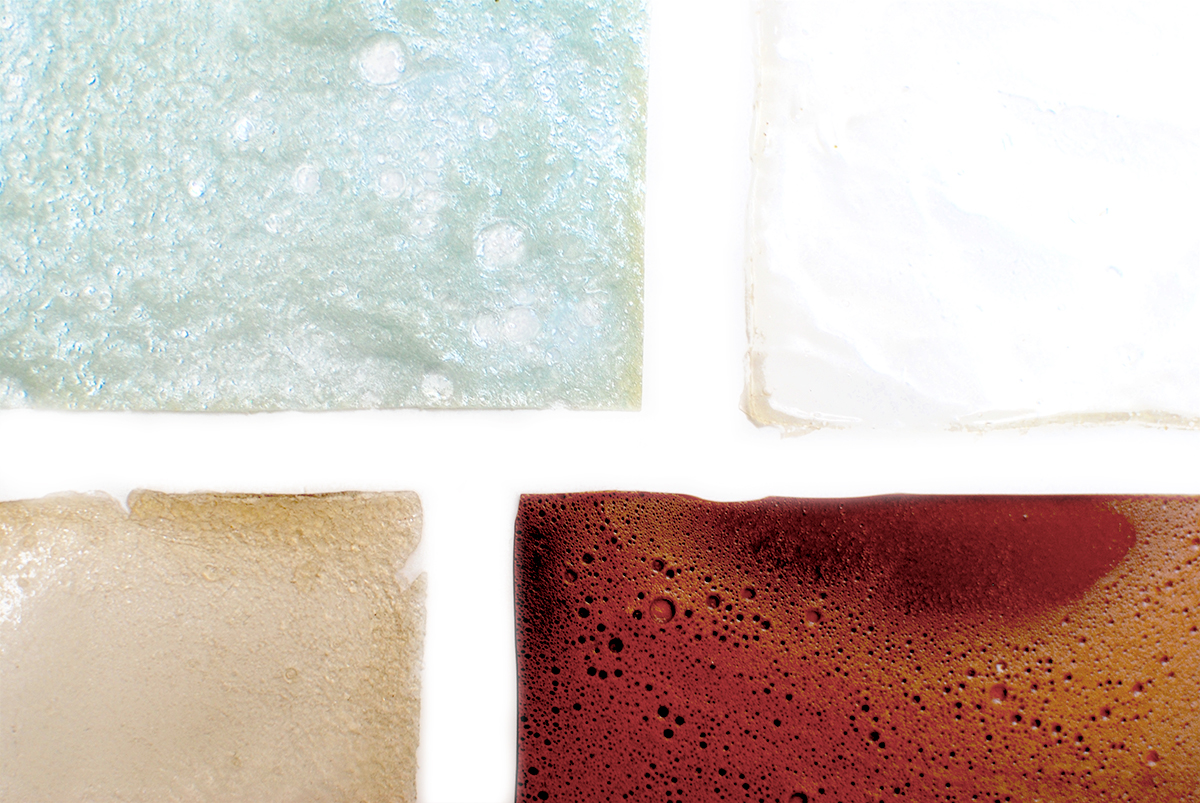
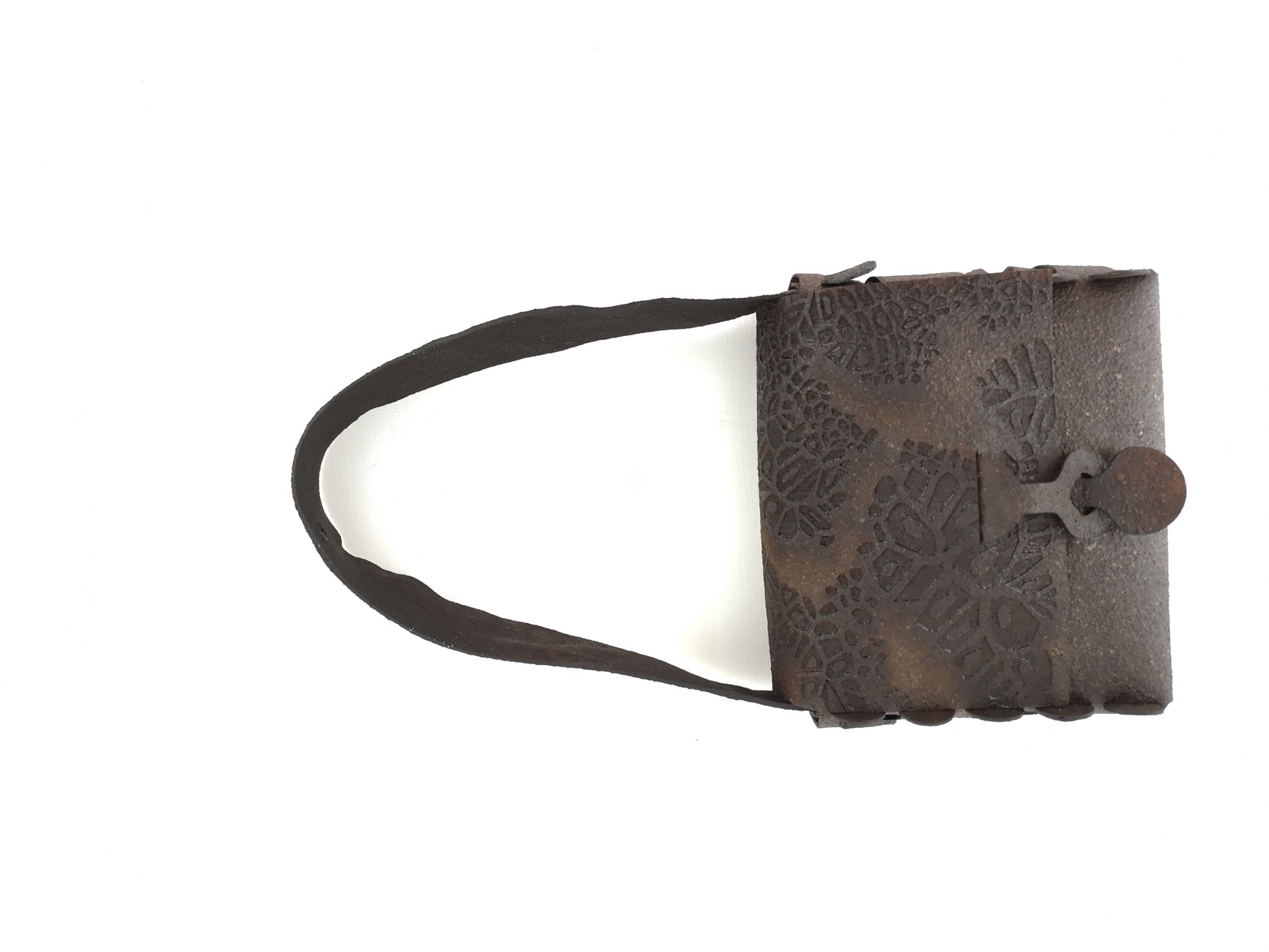
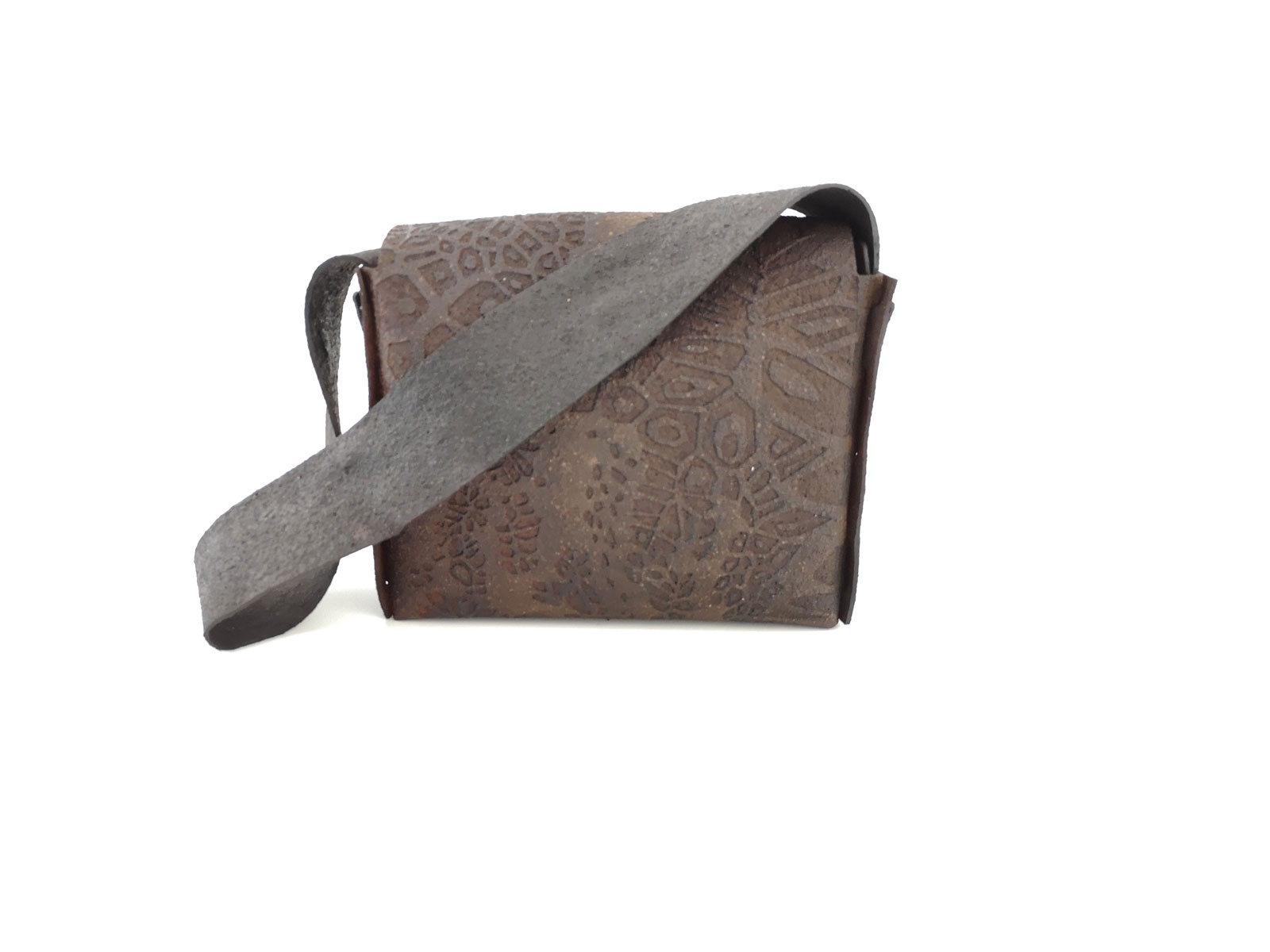
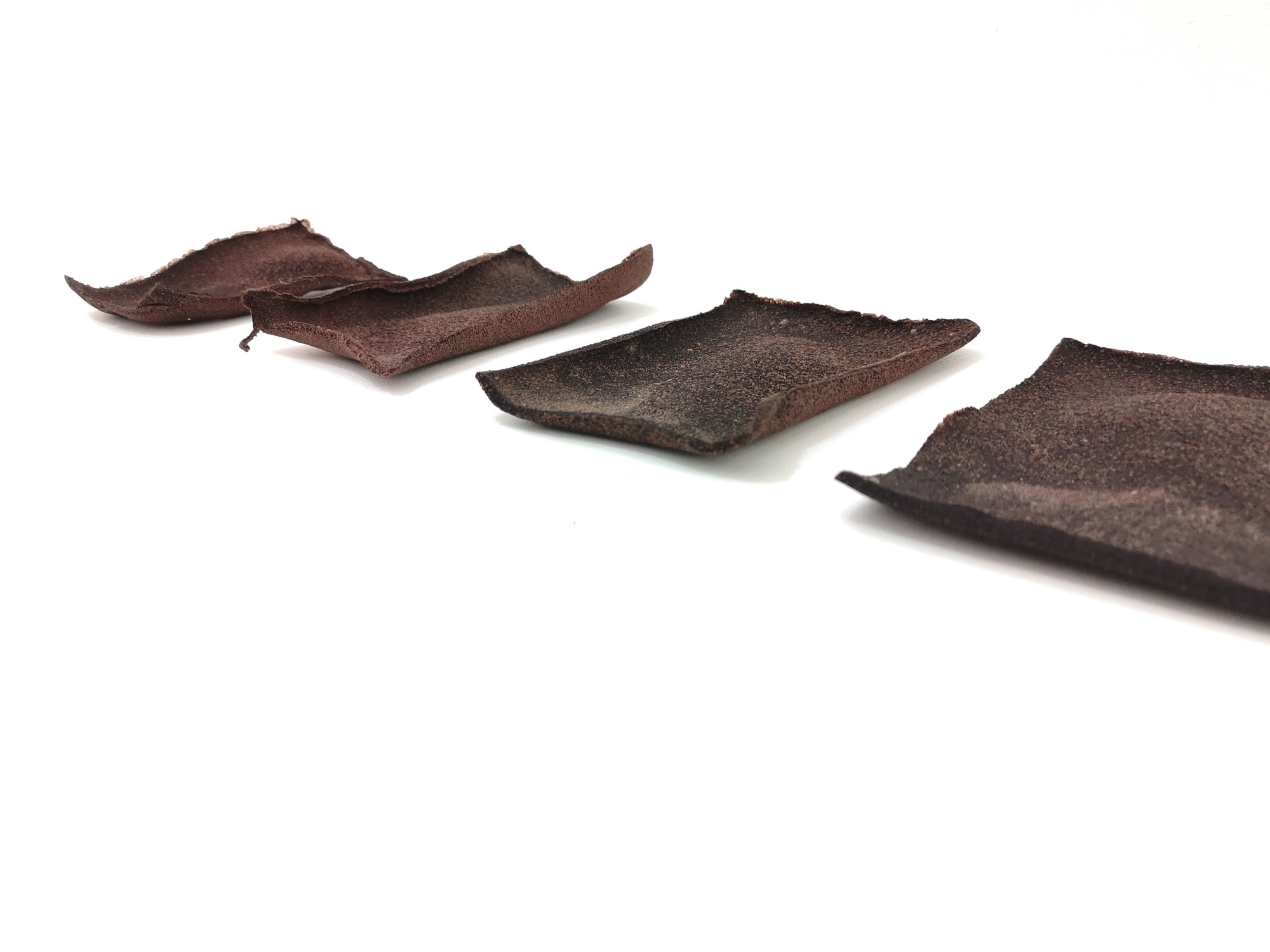
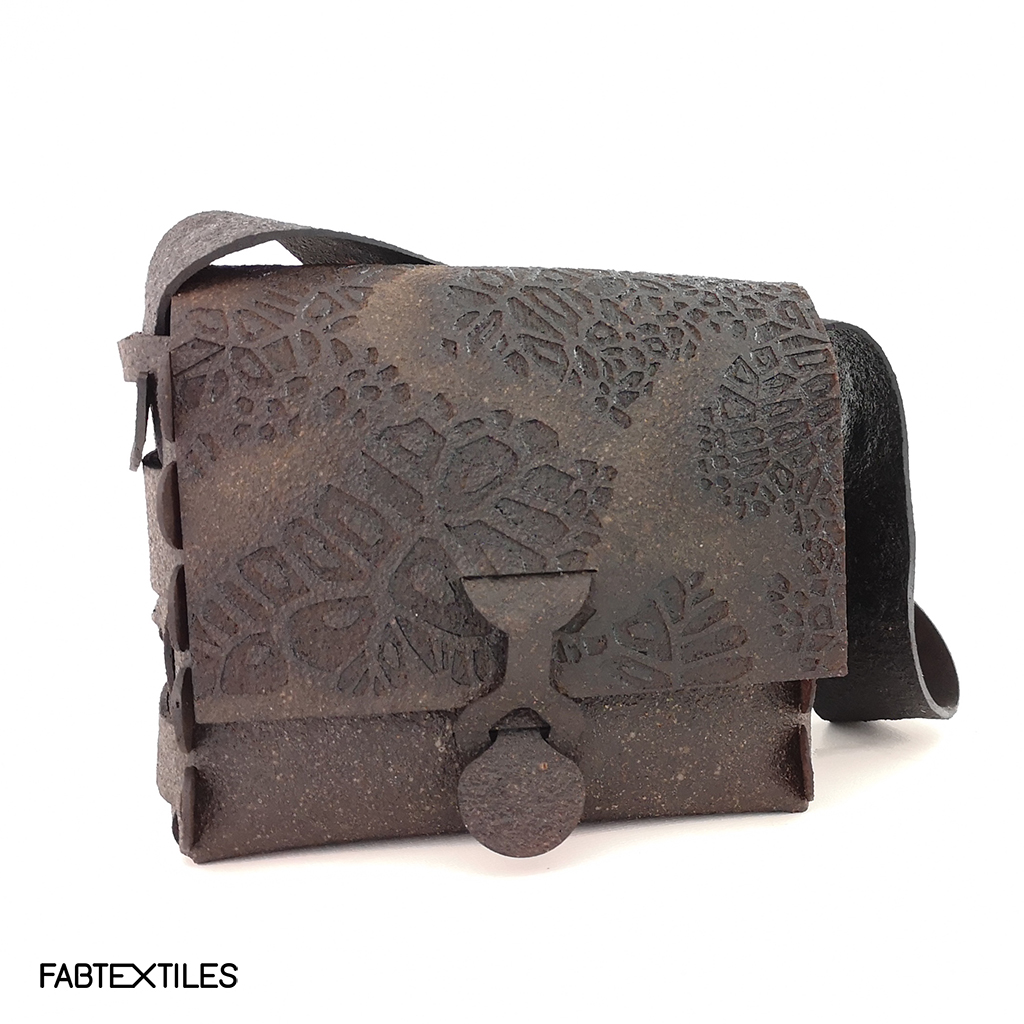
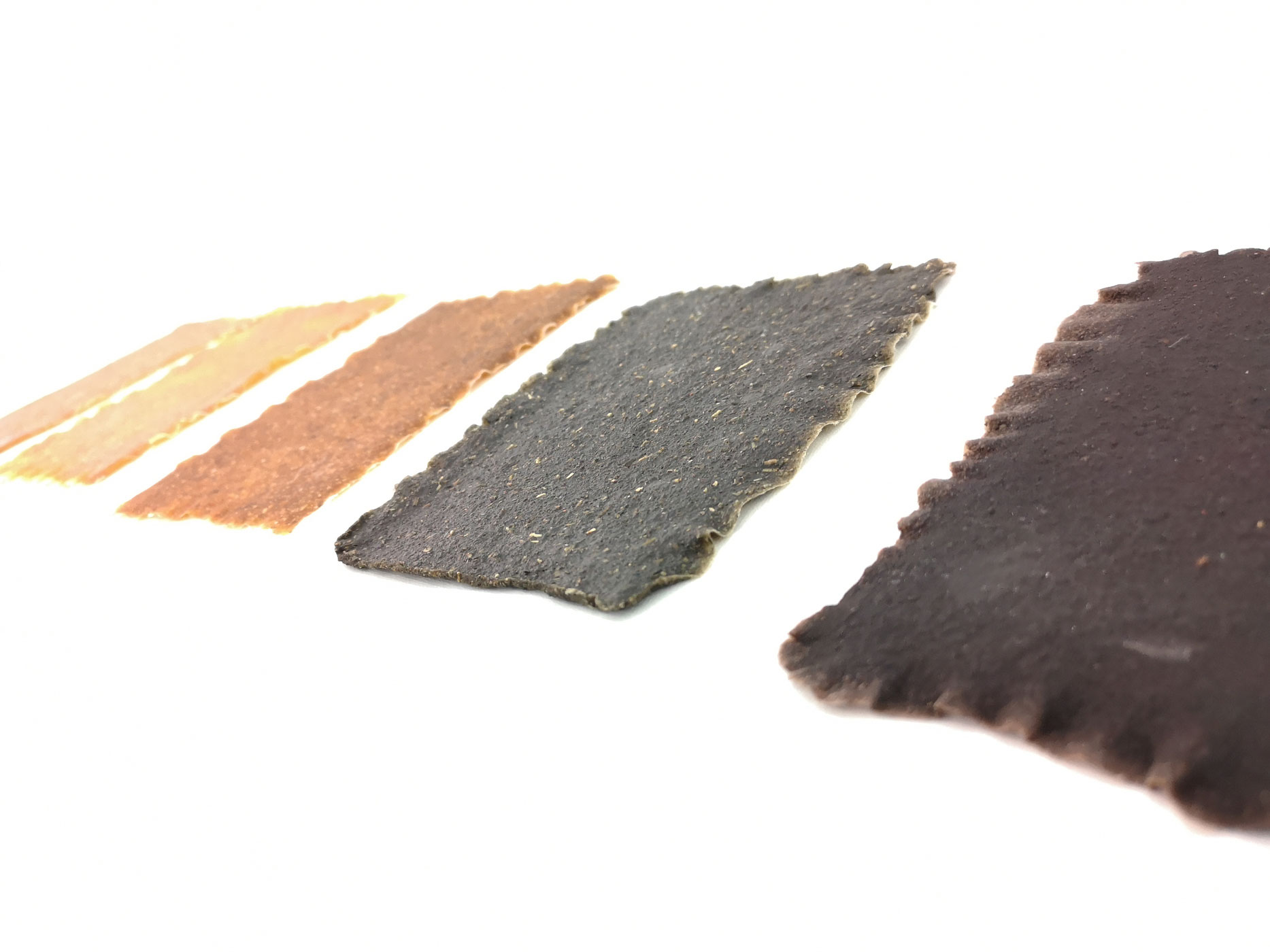
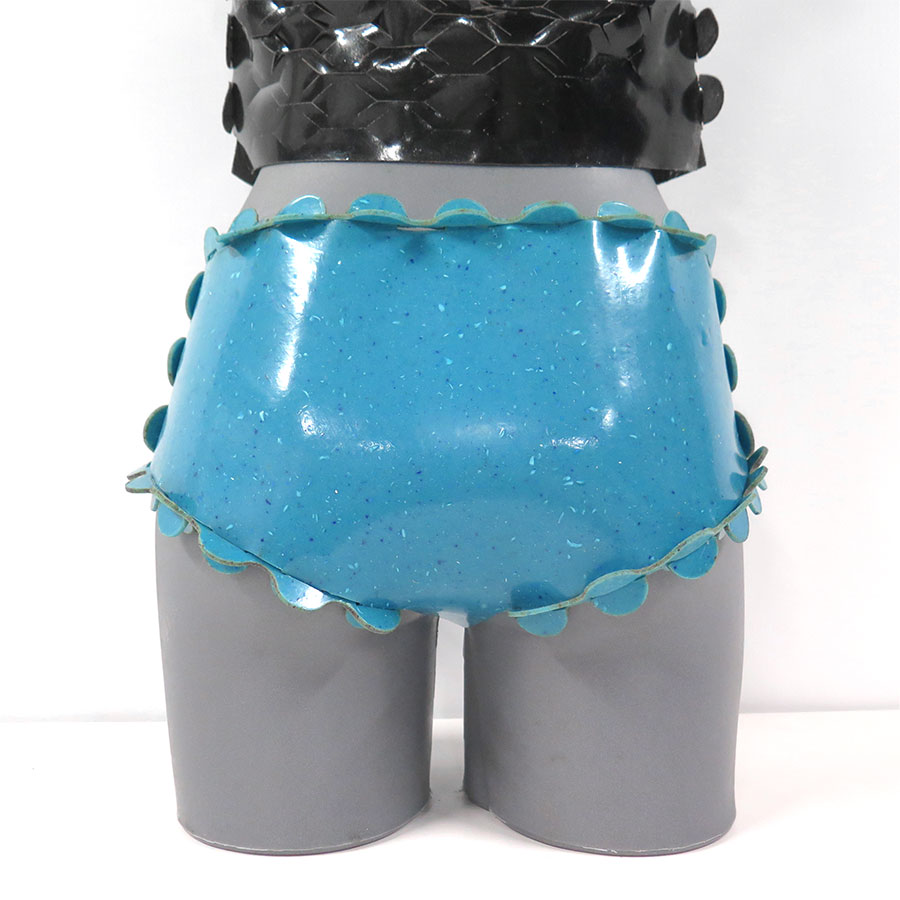
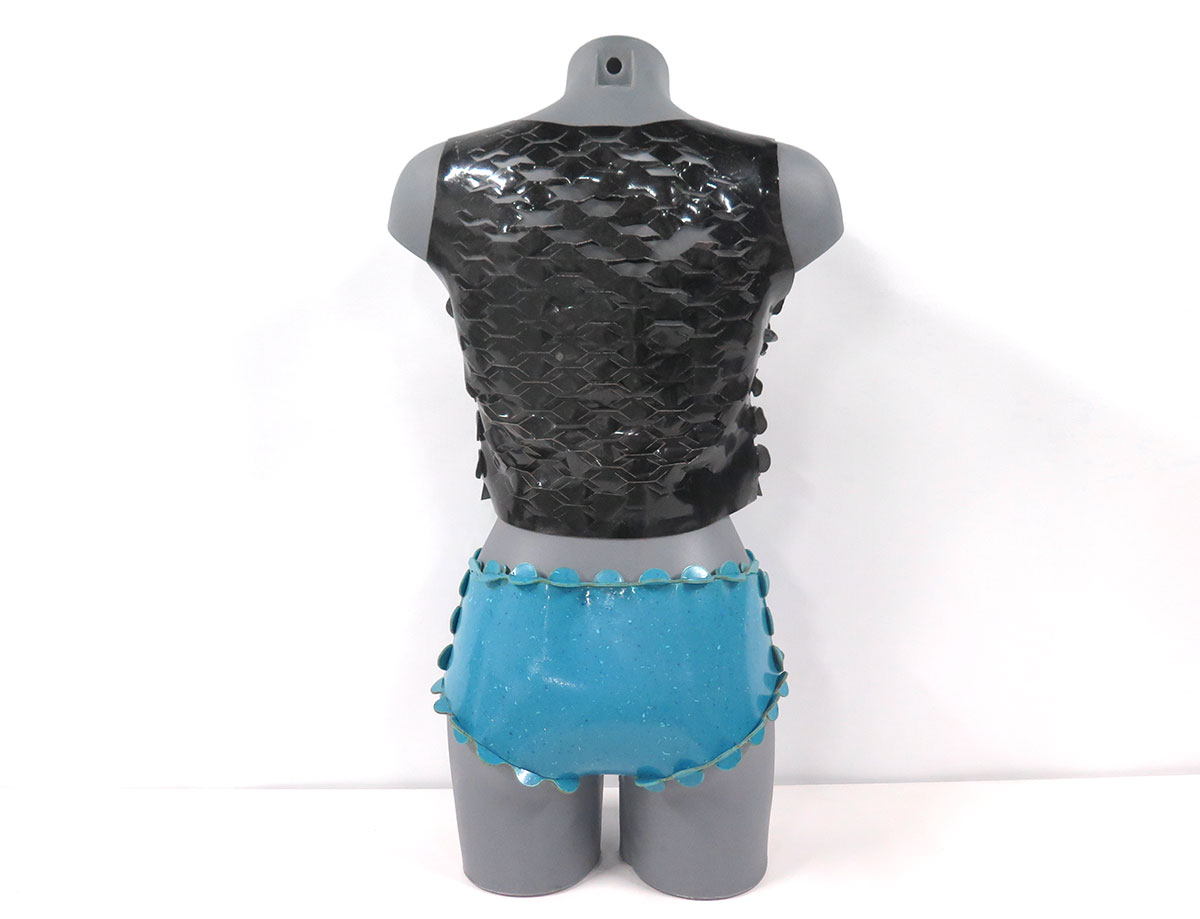
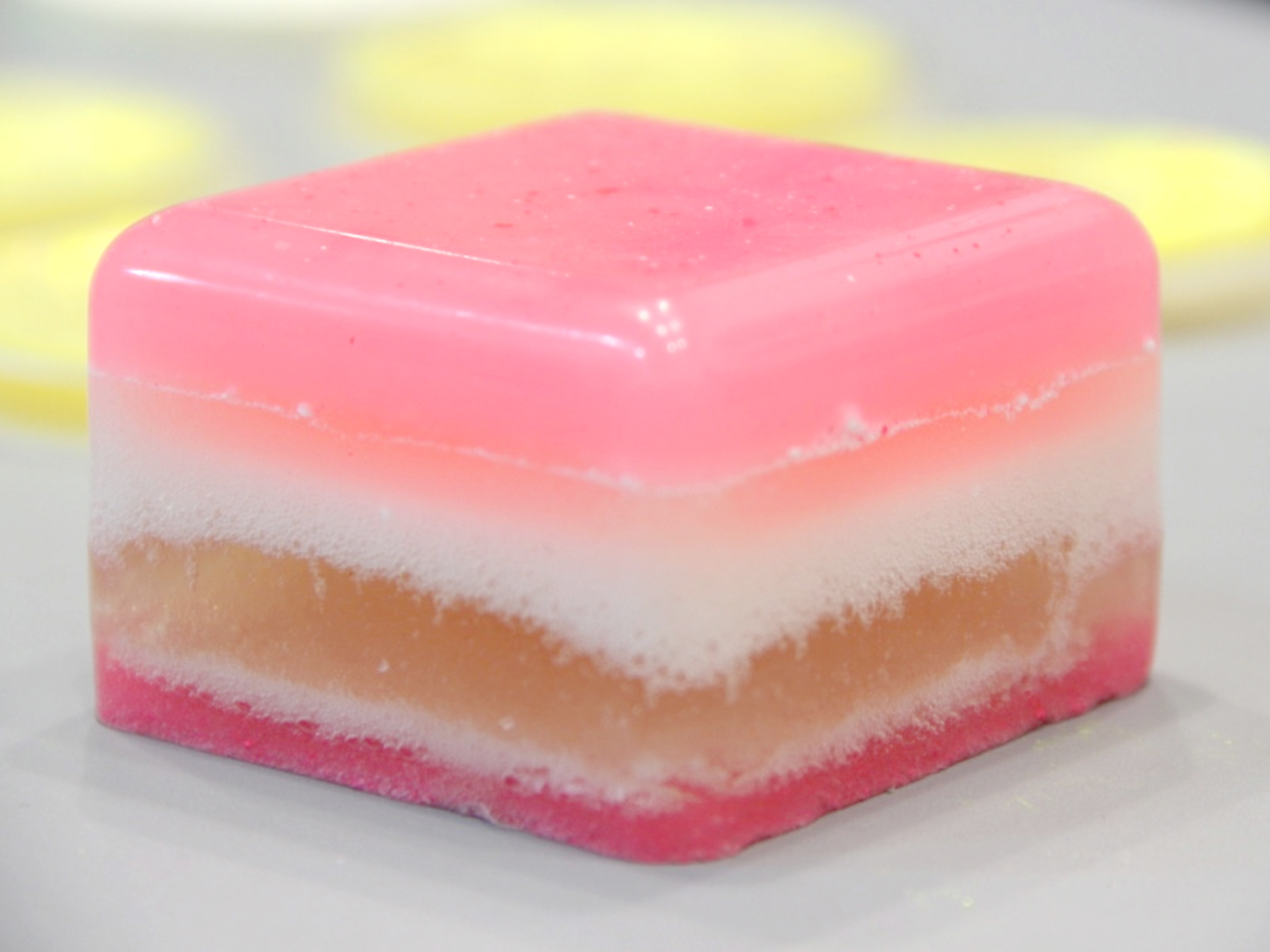
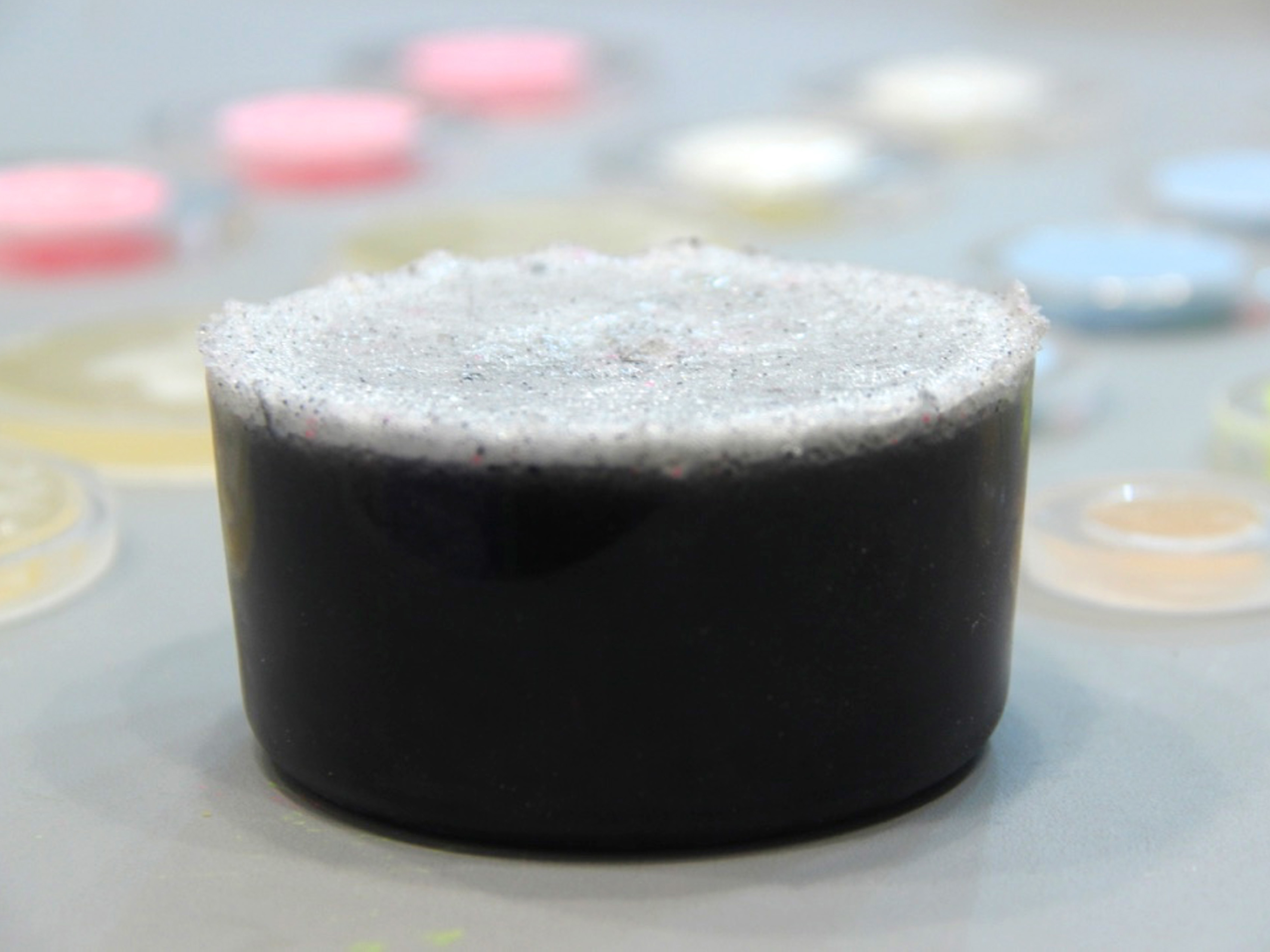
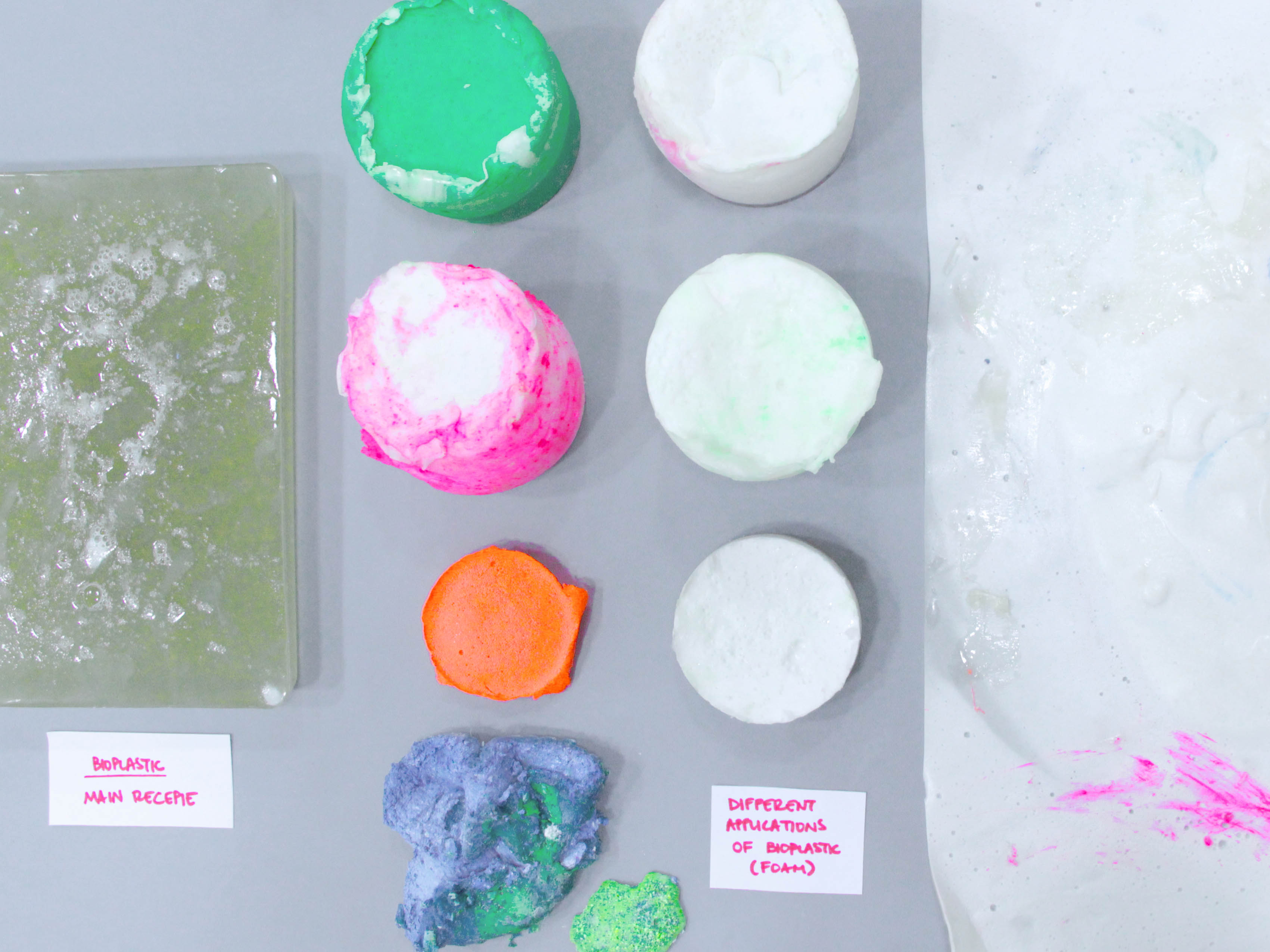
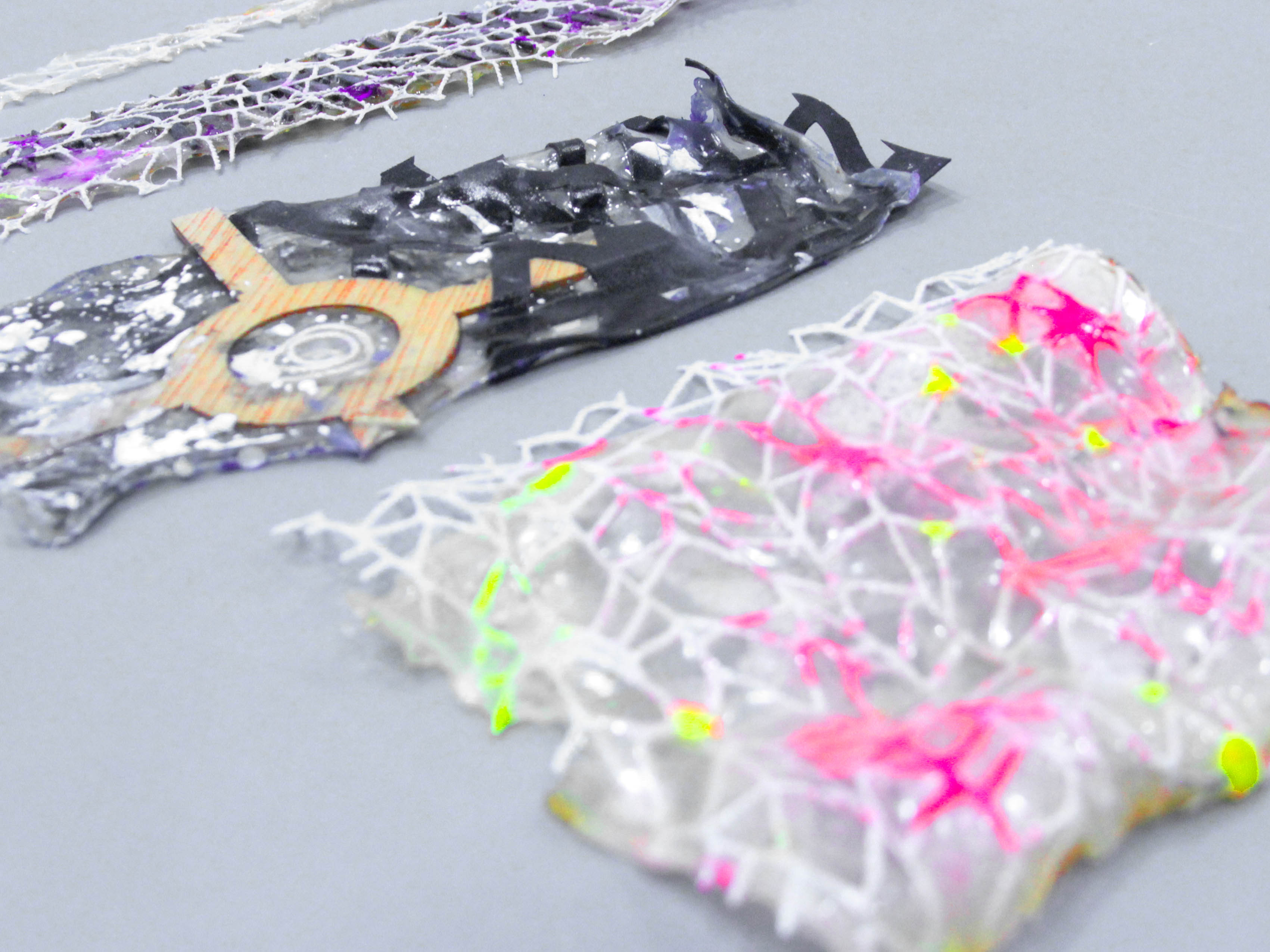
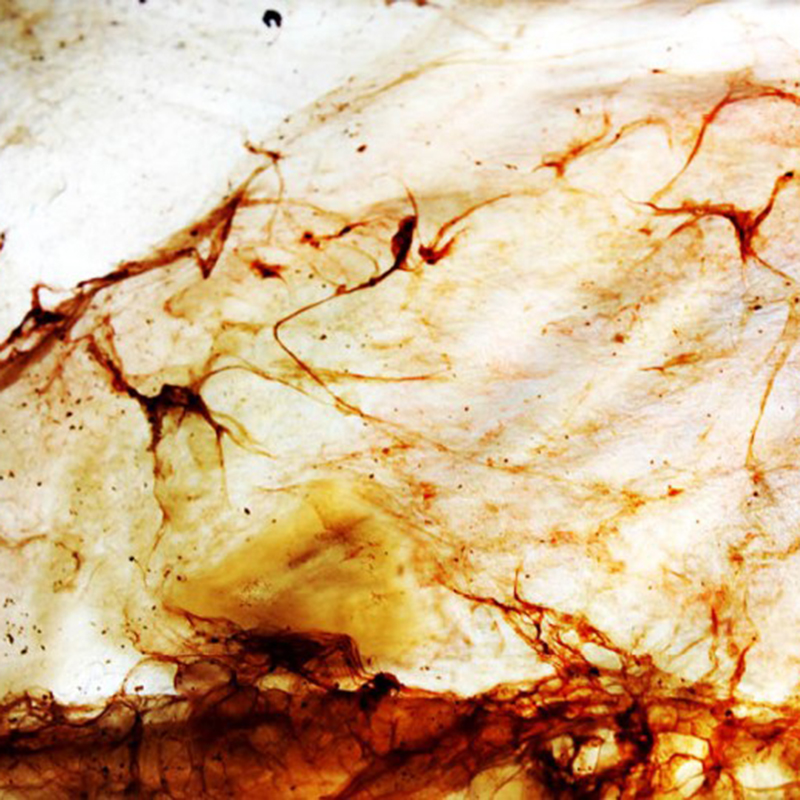
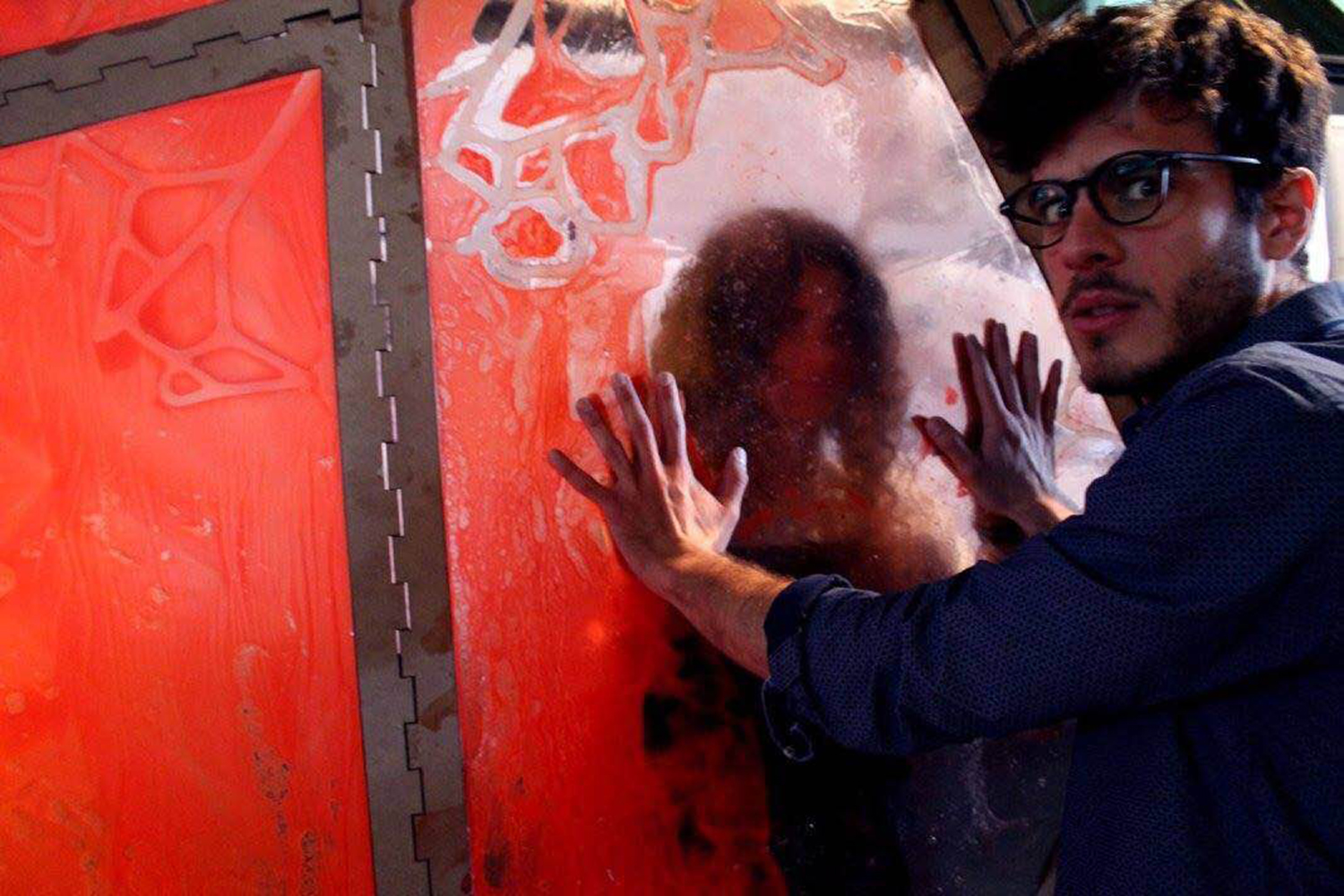
Bioplastics samples by Margaret Dunne, FabTextiles, Fab Lab Barcelona, 2018
.
During her two month internship at FabTextiles and Materials lab, Margaret Dunne, a fiber scientist researcher studying at the College of Human Ecology at Cornell University, contributed to the research and development bioplastic experimentation. Her task during the internship was to master Bioplastic recipes, experiment and amplify the materials catalogue and publish the second open source book of FabTextiles lab called The Bioplastic Cook Book.
.
After
The Secret of Bioplastics, written by Clara Davis in 2017, which explained the history of bioplastics,
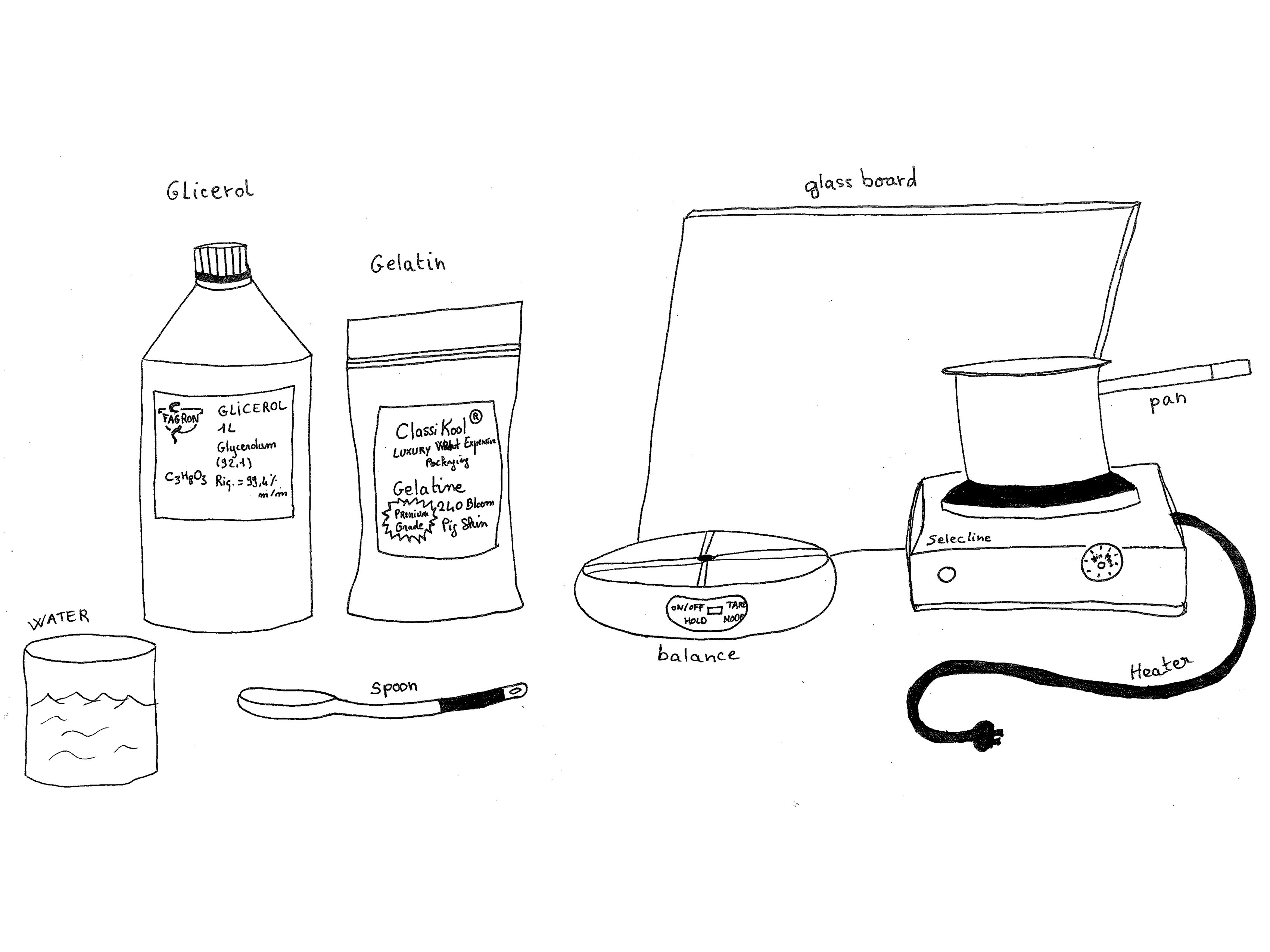
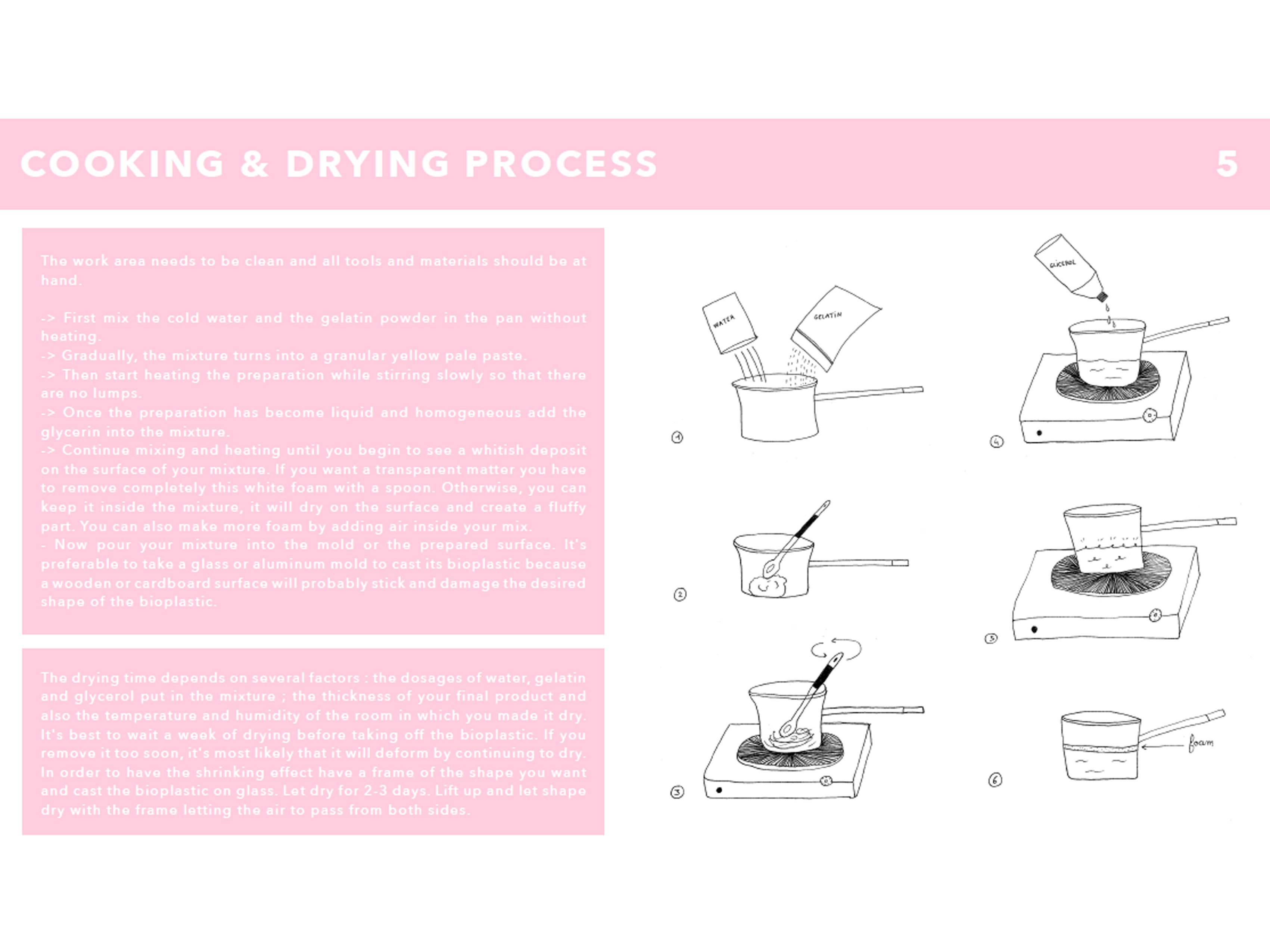
The Bioplastic Cook Book focuses on recipes for making bioplastics. You can find precise instructions for making gelatine, agar-agar and corn-starch-based bioplastics. Dunne also offers bio-composite recipes using clay, burlap and hemp.
.

Bioplastic cook book page by Margaret Dunne, FabTextiles, Fab Lab Barcelona, 2018
.
In the Bioplastic Cook Book every single ingredient is biodegradable. They are made with biopolymers, plasticizers, solvents, and sometimes an additional, additive. The book opens with the indispensible basics anybody with a passing interest ought to know, required reading before any attempt to make bioplastic. At the end, a question is posed : are bioplastics harmless to the environment ? Margaret Dunne atteimpts to address this problem, exploring the carbon footprint that results from bioplastics.
.

Bioplastic cook book page by Margaret Dunne, FabTextiles, Fab Lab Barcelona, 2018
.
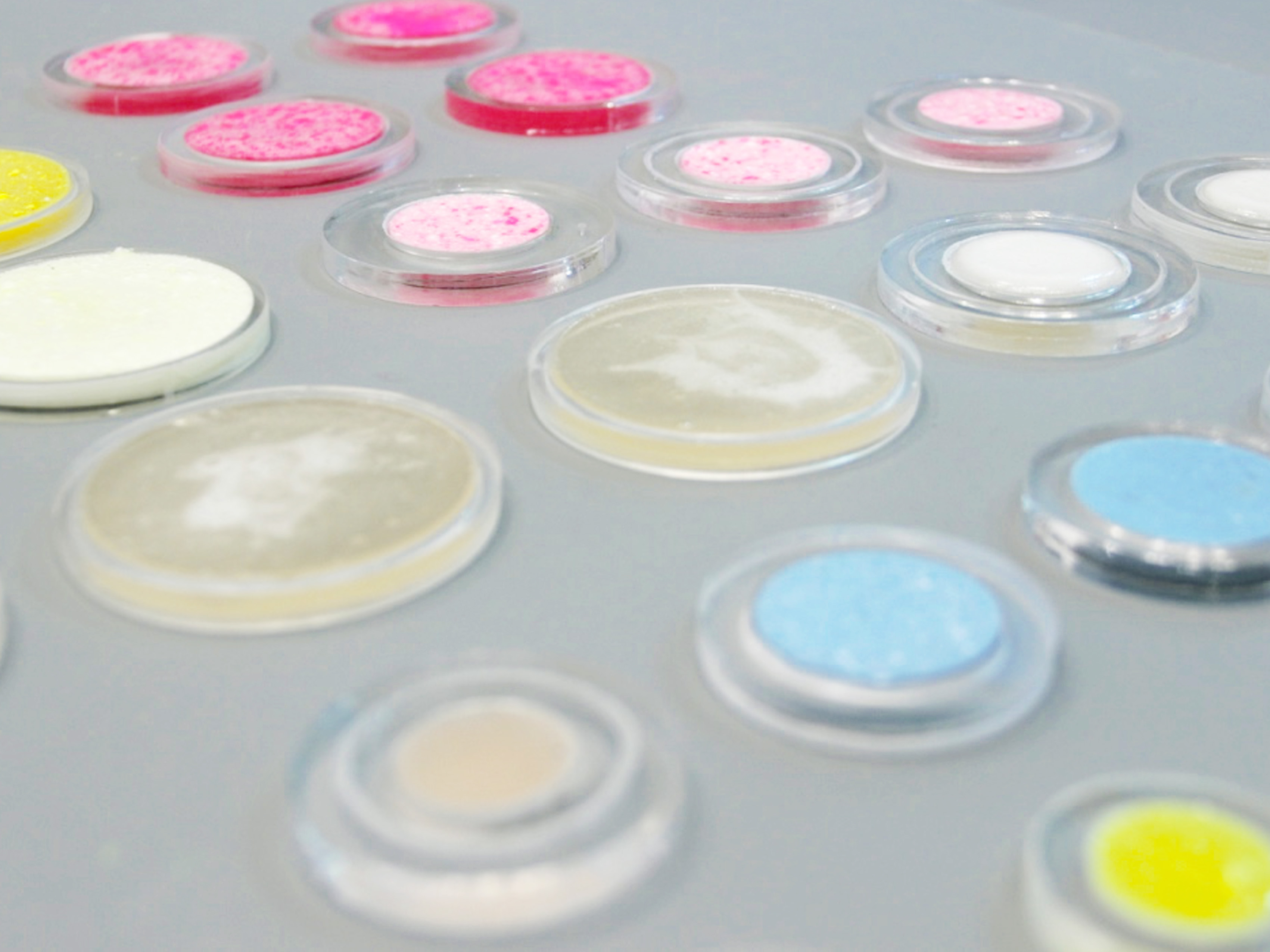
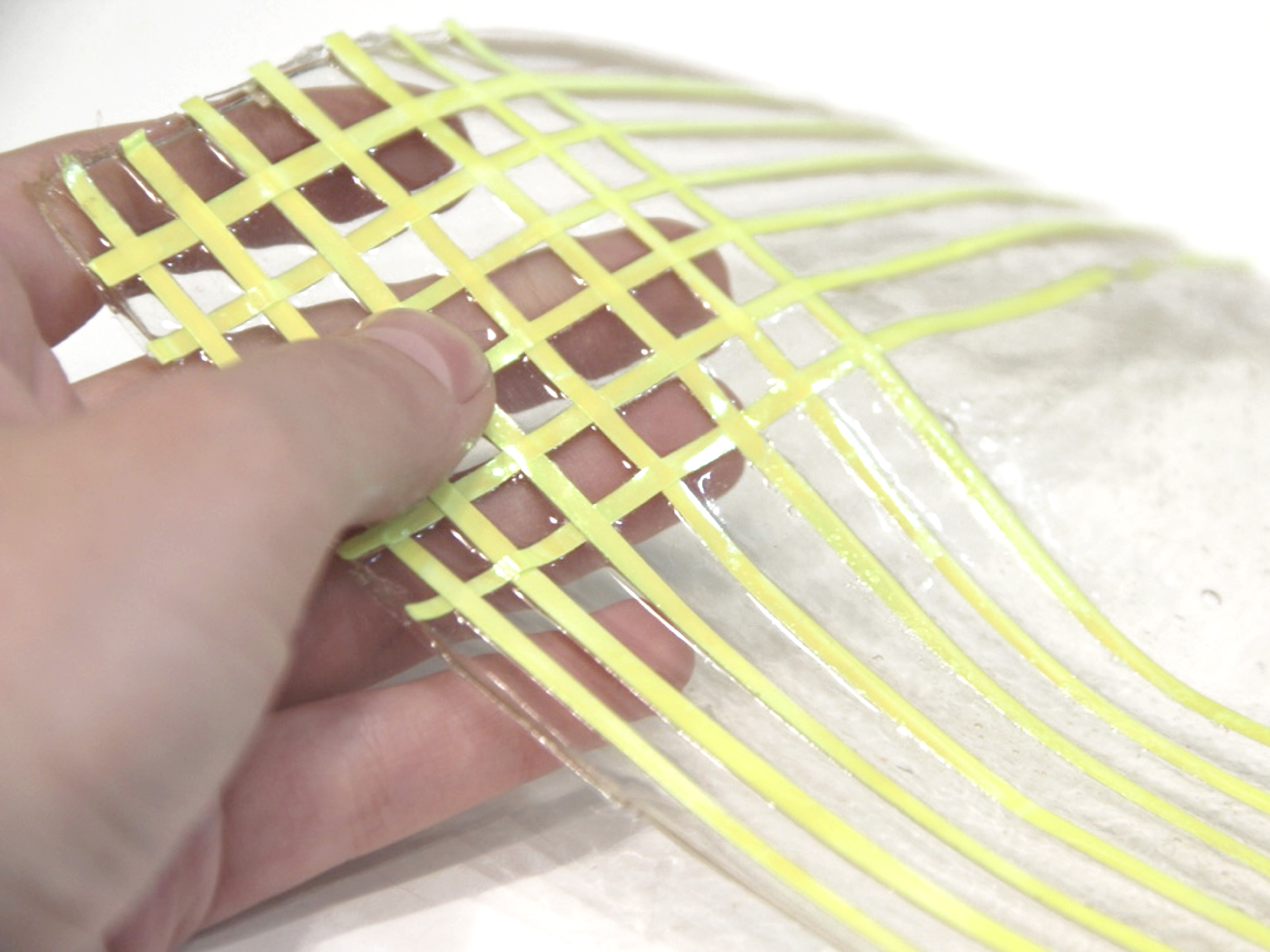
There is a link to the Bioplastic Cook Book at the end of this post. Below, some pictures of Margarette Dunne’s experiments.

Gelatine-based bioplastic sample by Margaret Dunne, FabTextiles, Fab Lab Barcelona, 2018
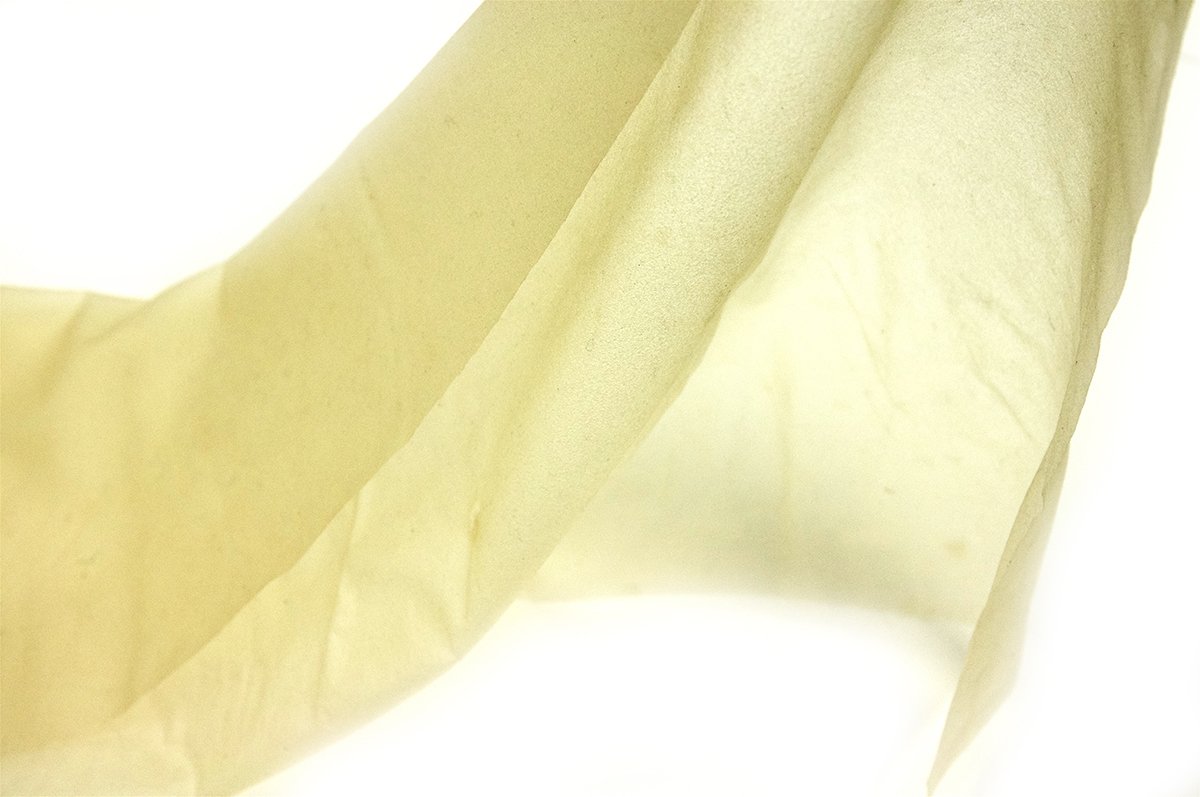

Agar-agar-based bioplastic sample by Margaret Dunne, FabTextiles, Fab Lab Barcelona, 2018
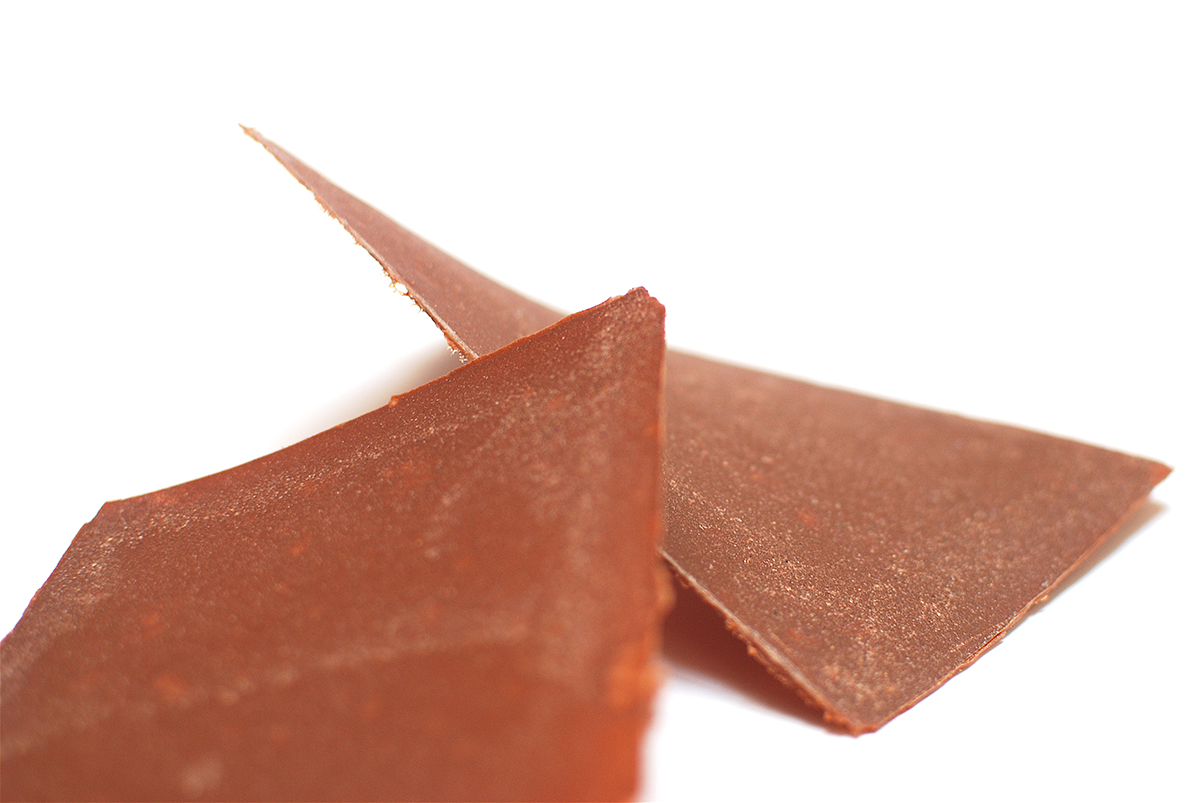

Bio-composite gelatine+clay sample by Margaret Dunne, FabTextiles, Fab Lab Barcelona, 2018
Bioplastic gelatine+spirulina sample by Margaret Dunne, FabTextiles, Fab Lab Barcelona, 2018
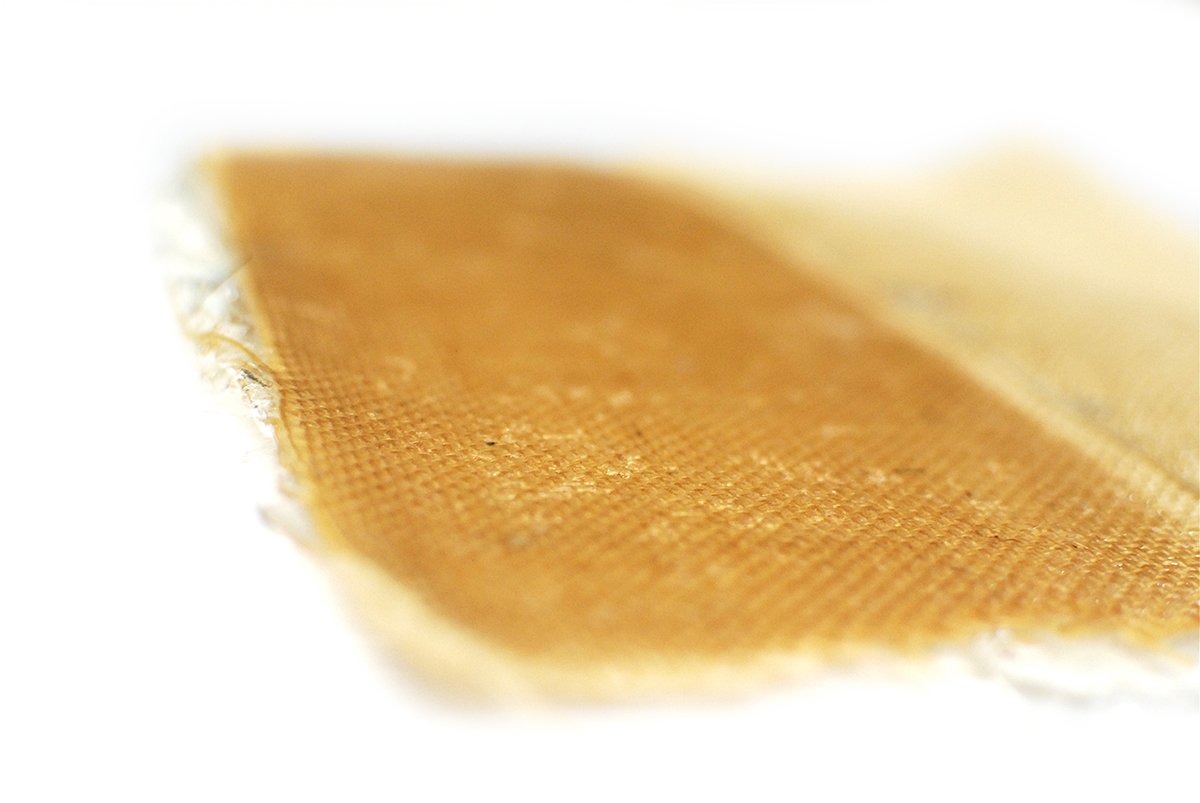

Bio-composite gelatine+burlap sample by Margaret Dunne, FabTextiles, Fab Lab Barcelona, 2018
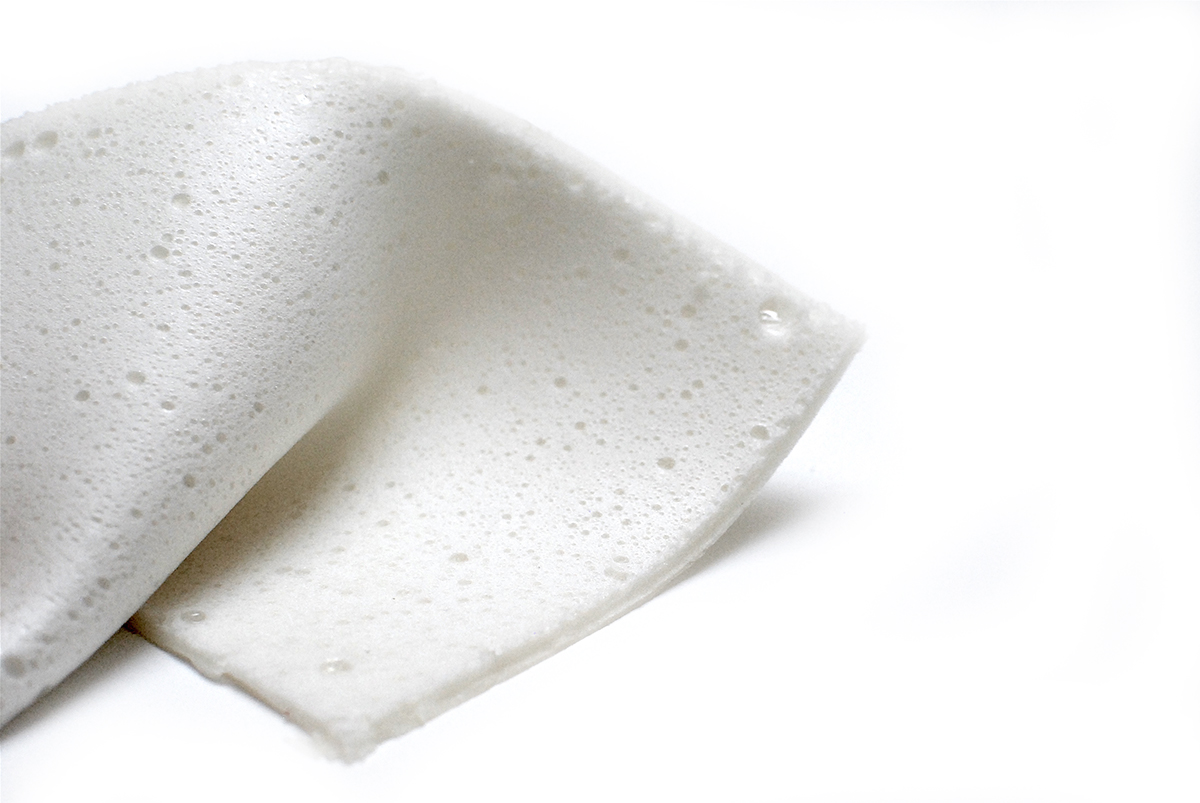

Bioplastic gelatine foam sample by Margaret Dunne, FabTextiles, Fab Lab Barcelona, 2018
.
Bioplastic cook book by Margaret Dunne, FabTextiles, Fab Lab Barcelona, 2018
.
.
And if you’d like to know more about the general history of bioplastics, when, where and why they were created you can check our first published book:
The Secrets of Bioplastics by Clara Davis here.
.
.